How Often To Water Tomatoes In Pots: A Comprehensive Guide For Optimal Growth
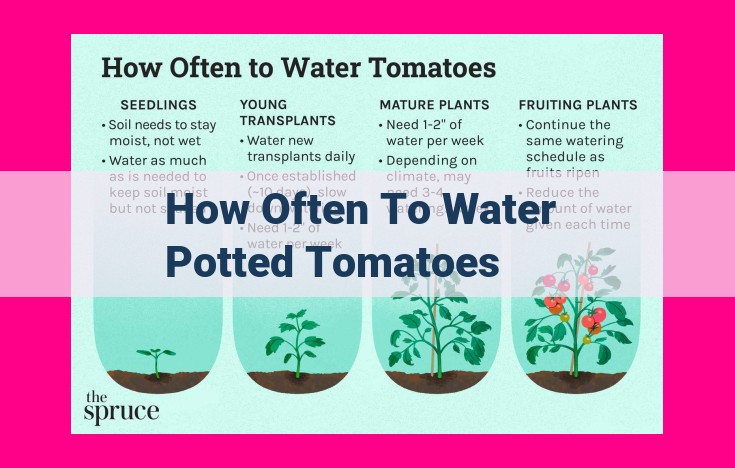
When growing tomatoes in pots, watering frequency depends on factors such as pot size, soil type, and environmental conditions. Generally, water your tomatoes deeply when the top few inches of soil are dry to the touch. Smaller pots require more frequent watering than larger ones, and well-draining soil dries out faster than heavier soil. During hot, dry weather, you may need to water every day or two, while in cooler or rainy conditions, watering once or twice a week may suffice. Use a moisture meter to check soil moisture levels to avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot.
Environmental Factors Impacting Plant Growth: Sunlight and Water
The captivating realm of plant growth is influenced by an intricate tapestry of environmental conditions. Among them, sunlight and water stand as indispensable forces, each playing a pivotal role in the harmonious development of our verdant companions.
Sunlight: The Photosynthesis Lifeline
Sunlight, a celestial treasure, serves as the primary energy source for plants. Through the remarkable process of photosynthesis, plants harness sunlight’s radiant powers to transform carbon dioxide and water into glucose, the vital fuel that propels their growth and sustenance. Sunlight duration, intensity, and quality all exert a profound influence on photosynthesis, directly impacting plant growth rates and overall well-being.
Water: The Elixir of Life
Water, the lifeblood of all living creatures, is no less crucial for plants. It comprises a significant portion of their weight, facilitates nutrient transport, and provides turgidity for structural support. Water availability, including watering frequency, quantity, quality, and irrigation method, profoundly affects plant growth and health. Plants that receive inadequate water may exhibit symptoms of stress, such as wilting, stunted growth, and premature leaf drop. Conversely, overwatering can lead to root rot and other detrimental effects.
Watering Frequency and Amount
The optimal watering schedule for plants varies depending on species, soil type, and environmental conditions. Generally, plants prefer regular, moderate watering to sporadic, heavy浇灌. The frequency between watering should allow the soil to dry out slightly before rehydrating, as this promotes root development and prevents waterlogging. The amount of water applied should be sufficient to moisten the soil thoroughly without creating waterlogged conditions.
Water Quality and Irrigation Method
Water quality, influenced by factors such as pH, salinity, and mineral content, can also impact plant growth. Plants have varying tolerances to different water qualities, and some may be sensitive to certain impurities or chemical treatments. The irrigation method employed, whether manual watering, drip irrigation, or soaker hoses, should ensure even distribution of water to the root zone while minimizing water loss through evaporation or runoff.
By comprehending the essential roles of sunlight and water in plant growth, we can tailor our care and cultivation practices to nurture thriving, vibrant specimens that add beauty and vitality to our environments.
Influence of Physical Factors on Plant Growth
Beyond environmental conditions, physical factors also play a pivotal role in determining the health and growth of your plants. Understanding the impact of these factors and optimizing them can enhance your plants’ well-being and growth potential.
Plant Size and Growth Rate
The size of a plant is not just an indicator of its maturity but also directly correlates with its growth rate and nutrient requirements. As a plant grows larger, it naturally requires more resources to support its expanded size. As a result, larger plants need more sunlight, water, and nutrients to maintain their growth trajectory.
Soil Type and Plant Health
The type of soil in which your plants grow has a significant influence on their health and growth. Different soil types vary in their drainage, texture, nutrient content, and pH levels. These variations can affect the plant’s ability to absorb nutrients, retain moisture, and develop healthy roots. Understanding the specific needs of your plants and choosing the appropriate soil type is crucial for optimal growth.
Pot Size and Root Development
For container-grown plants, pot size becomes a determining factor for root development and overall growth. A pot that is too small can restrict root growth, limiting the plant’s ability to absorb nutrients and water. Conversely, a pot that is excessively large can lead to waterlogging and root rot. Selecting an appropriate pot size is essential for ensuring healthy root development and promoting overall plant growth.
Soil Drainage and Optimal Moisture Levels
Soil drainage is critical for plant health. Excess water in the soil can lead to root rot and other problems. Good drainage allows excess water to flow away from the roots, ensuring that they receive the oxygen they need to function properly. You can use a soil moisture meter to monitor soil moisture levels and ensure they are neither too wet nor too dry for optimum plant growth.