Ultimate Guide To Home Generators: Powering Your Home Through Outages
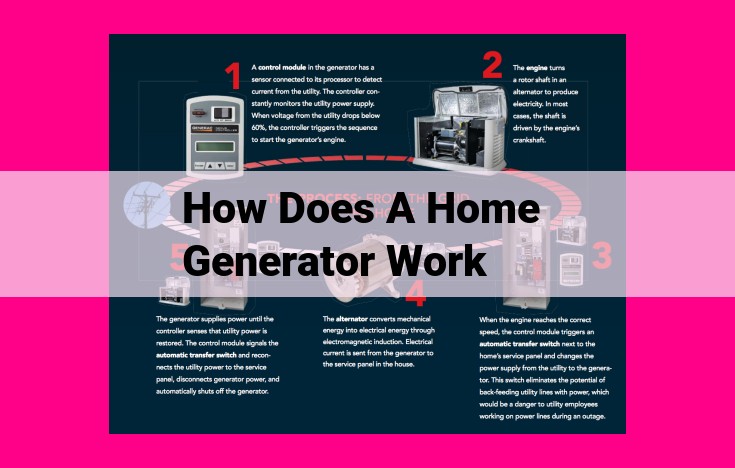
A home generator works by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy to provide backup power during grid outages. Key components include the engine, which provides mechanical energy, and the alternator, which converts it into electricity. The transfer switch ensures a safe transition from grid power to generator power. Portable generators are suitable for emergency use, while standby generators offer automatic power backup. Inverter generators provide clean power for sensitive electronics. Fuel options include gasoline, propane, and natural gas. Essential considerations include wattage requirements, capacity, regular maintenance, and load management to prevent overloading.
The Mighty Engine: The Heartbeat of Your Generator
In the world of generators, the engine reigns supreme as the driving force behind its power-generating capabilities. Just like the human heart, the engine is the core of the generator, responsible for converting fuel into the mechanical energy that ultimately produces electricity.
When selecting a generator, understanding the different engine types is crucial. Let’s dive into the three primary engine options:
-
Diesel Engines: These heavy-duty engines are known for their durability and efficiency. They offer extended runtimes on a single tank of fuel, making them ideal for prolonged power outages. Diesel generators also pack a higher power output than their gasoline counterparts.
-
Gasoline Engines: These are the most common engine type for portable generators. Gasoline generators are relatively lightweight and affordable, making them a popular choice for recreational purposes or emergencies. However, they have a shorter lifespan and lower fuel efficiency than diesel engines.
-
Propane Engines: Propane generators offer a clean-burning alternative to gasoline. They’re a great option for indoor use due to their reduced emissions. Propane tanks provide a convenient and portable way to store fuel, ensuring longer runtimes during power outages.
Alternator: Explain the function of the alternator in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
The Heart of a Generator: The Alternator
In the world of electricity, the alternator reigns supreme as the centerpiece of any generator. This unsung hero performs the remarkable task of transforming raw mechanical energy into the electrical power that fuels our homes and businesses.
Imagine a generator as a miniature power plant. Inside its sturdy frame resides an engine that roars with life, spinning a rotor at lightning-fast speeds. As the rotor whirls, it glides past a series of stationary coils known as the stator. This interaction creates a dance of magnetic fields that induces a flow of electrons in the stator coils.
This flow of electrons constitutes an alternating current (AC), meaning that the direction of the electrical flow reverses periodically. To harness this AC power for our needs, the generator employs a rectifier that transforms it into direct current (DC) – the type of electricity that runs our appliances and devices.
The alternator’s capacity to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy is astonishing. It’s the heart of the generator, the maestro that orchestrates the seamless flow of power to our devices. Without it, our world would be shrouded in darkness and silence.
Transfer Switch: The Power Orchestrator of Your Generator
In the realm of power generation, the transfer switch plays a crucial role, akin to a conductor in an orchestra, orchestrating the seamless flow of electricity from the grid to your generator. This ingenious device ensures that when a power outage strikes, your generator seamlessly steps into the limelight, powering your vital appliances and keeping your home or business humming along.
Imagine this: you’re enjoying a cozy evening at home, immersed in your favorite TV show, when suddenly the lights flicker and plunge you into darkness. Frustration washes over you, but then, like a beacon of hope, your generator roars into action. However, how does it know when to do its magic? That’s where the transfer switch comes in.
The transfer switch is a smart device that monitors the grid’s power supply. When it senses a power outage, it automatically disconnects your home from the grid. This is crucial because if your generator is connected to the grid while it’s running, it could potentially send electricity back into the grid, which can be dangerous for utility workers.
Once the transfer switch has isolated your home from the grid, it swiftly connects you to your generator. This process usually takes a matter of seconds, ensuring that your power outage is as brief and painless as possible.
There are two main types of transfer switches:
- Manual transfer switches: These switches require you to manually start the generator and then throw a switch to connect it to your home.
- Automatic transfer switches: These switches automatically start the generator and connect it to your home when a power outage occurs.
Automatic transfer switches are more convenient, but they are also more expensive than manual transfer switches.
No matter which type of transfer switch you choose, it’s essential to have it installed by a **licensed electrician. Improper installation can lead to electrical hazards, so it’s best to leave this task to a professional.**
**Fuel Tank: The Lifeline of Your Generator**
When the lights go out and the power grid falters, your generator becomes a lifeline, providing essential electricity to power your home or appliances. But without a steady supply of fuel, your generator is as useless as a paperweight. This is where the fuel tank comes into play.
Fuel Tank Sizes and Capacities
Fuel tanks for generators come in a variety of sizes, from small, portable tanks to large, stationary tanks. The size of the tank you choose will depend on several factors, including the size of your generator, the amount of power you need, and the length of time you need the generator to run.
Small, portable tanks are ideal for generators used in emergencies or for short-term power outages. They can typically hold a few gallons of fuel and provide power for several hours. Larger, stationary tanks are better suited for generators that are used as a backup power source for your home or business. They can hold hundreds of gallons of fuel, providing days or even weeks of power during extended outages.
Importance of Fuel Storage
Proper fuel storage is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of your generator. Here are a few tips to keep in mind:
- Store fuel in a cool, dry place. Heat and moisture can cause fuel to degrade and lose its potency.
- Use a fuel stabilizer. This additive can help prevent fuel from going stale and extend its shelf life.
- Keep fuel containers tightly sealed. This will prevent evaporation and contamination.
- Inspect your fuel regularly. Look for signs of leaks, discoloration, or sediment.
Running on Empty
Nothing is more frustrating than running out of fuel when you need your generator the most. To avoid this scenario, it’s important to monitor your fuel level regularly and refuel your generator before it runs out completely. If your generator does run out of fuel, never attempt to refuel it while it is running. Allow the generator to cool down completely before adding more fuel.
Remember: A well-maintained fuel tank is an essential component of a reliable generator. By following these tips, you can ensure that your generator is always ready to provide power when you need it most.
Cooling system: Explain how the cooling system keeps the generator from overheating.
The Guardian of Cool: The Cooling System that Safeguards Your Generator
Just as a car engine requires a cooling system to prevent overheating, so does a generator. The cooling system in a generator plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures and preventing damage caused by excessive heat.
Imagine your generator as a tireless worker, toiling away to provide electricity when you need it most. But like any hard worker, it needs to cool down to avoid burnout. The cooling system acts as a heat disperser, keeping the generator’s components from overheating.
The typical cooling system in a generator consists of several key components: a radiator, a cooling fan, and coolant. The radiator is the heart of the system, acting as a heat exchanger. Hot coolant from the engine flows into the radiator, where it dissipates its heat into the surrounding air.
The cooling fan plays an equally important role by circulating air over the radiator’s surface, promoting efficient heat transfer. The coolant, usually a mixture of water and antifreeze, absorbs heat from the engine and carries it to the radiator, where it cools down and returns to the engine.
Maintaining a balanced temperature is essential for the generator’s longevity. Excessive heat can damage components, leading to costly repairs or even complete failure. The cooling system ensures that the generator operates within its optimal temperature range, minimizing the risk of overheating and ensuring your power source remains reliable when you need it most.
Electrical Panel: The Heart of Your Generator’s Power Distribution
As the backbone of your generator’s electrical system, the electrical panel is a crucial component that ensures the safe and efficient distribution of power to your appliances and devices. It houses a symphony of electrical components, each playing a vital role in safeguarding against overloads and delivering reliable electricity.
Breakers: The Gatekeepers of Power
Imagine these “breakers” as vigilant guardians, constantly monitoring the electrical flow. If the current exceeds a safe level, they swiftly and decisively trip, interrupting the flow of electricity to prevent damage to your equipment. This automated defense mechanism ensures the safety and longevity of your prized possessions.
Fuses: Selfless Sacrifices for Protection
Fuses are unsung heroes in the electrical panel’s defense system. These sacrificial elements contain a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit under excessive current, preventing hazardous surges from reaching your devices. By sacrificing themselves, fuses protect your appliances and the integrity of your generator.
Voltage Regulator: Ensuring a Steady Flow
The voltage regulator is a meticulous maestro that maintains a consistent voltage level throughout the electrical system. This unwavering stability is essential for the smooth operation of your appliances, preventing voltage fluctuations that could cause malfunction or damage.
Surge Protector: Shielding from Electrical Storms
Like a valiant knight in shining armor, the surge protector stands as a formidable defender against sudden surges of electricity. These unwelcome transients can wreak havoc on your electronics, but the surge protector, with its rapid-response capabilities, absorbs these jolts and diverts them harmlessly away, shielding your precious devices from harm.
Portable Generators: Emergency Power or Camping Companions
In the face of power outages or the allure of outdoor adventures, portable generators emerge as indispensable tools. They provide a lifeline of electricity, ensuring you’re either prepared for the unexpected or enjoying the comforts of home away from home.
Portable generators, as their name suggests, are designed for easy transportation and setup. They come in various sizes and capacities to cater to different power needs. Their compact design makes them ideal for quick deployment in emergencies or convenient use on camping trips.
One of the key considerations when choosing a portable generator is its wattage. This determines the amount of electrical load it can handle. It’s crucial to assess the wattage requirements of the appliances you intend to power to ensure the generator has sufficient capacity.
Another essential aspect is fuel type. Portable generators typically run on gasoline or propane. Gasoline generators offer wider availability, but propane generators have the advantage of providing cleaner emissions and longer storage life.
When using portable generators, safety is paramount. Always operate the generator in well-ventilated areas, away from open flames or enclosed spaces. Be mindful of exhaust fumes and ensure proper grounding to prevent electrical shocks.
Additionally, regular maintenance is essential to extend the life of your portable generator. This includes changing the oil, replacing air filters, and cleaning the spark plugs. By adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, you can keep your generator running smoothly and reliably.
Portable generators truly embody versatility. They provide peace of mind during power outages, empowering you with backup electricity. Be it for emergencies or camping adventures, these compact powerhouses ensure you’re never left in the dark.
Uninterrupted Power with Standby Generators: A Lifeline During Outages
As the world grows increasingly reliant on electricity, power outages can be more than an inconvenience – they can be a disruption to our lives, safety, and livelihoods. That’s where standby generators step in, providing peace of mind with their automatic power backup during outages.
Standby generators are permanent installations, typically connected to your home’s electrical system and a natural gas or propane line. When a power outage occurs, they automatically start up within seconds, seamlessly supplying your home or business with electricity. This uninterrupted power ensures that essential appliances, medical equipment, and communications systems remain operational, keeping you comfortable and connected.
Benefits of Standby Generators:
- Peace of mind: Knowing that your home or business will have power during an outage provides a sense of security and comfort.
- Protection for sensitive electronics: Standby generators produce clean and stable power, safeguarding your computers, appliances, and other sensitive equipment from damage.
- Automatic operation: No need to manually start or stop the generator – it does it all for you, providing hassle-free power restoration.
- Fuel efficiency: Standby generators are fuel-efficient, using only what’s necessary to maintain power, saving you money on operating costs.
- Long-term reliability: With proper maintenance, standby generators can provide reliable power for years to come, ensuring uninterrupted operation during unexpected outages.
Choosing the Right Standby Generator:
To ensure your standby generator meets your specific needs, consider the following factors:
- Wattage: Determine the total wattage of the appliances and equipment you need to power during an outage.
- Capacity: Choose a generator with a sufficient capacity to handle the wattage requirements of your connected devices.
- Fuel source: Consider natural gas or propane as fuel options, depending on availability and cost in your area.
- Installation: Consult with a licensed electrician to ensure proper installation and connection to your electrical system.
With a standby generator in place, you can rest assured that you’ll “weather the storm” of power outages without missing a beat. Enjoy uninterrupted power, peace of mind, and protection for your valuable devices, ensuring a comfortable and secure living or working environment.
Inverter generators: Describe the advantages and disadvantages of inverter generators, which produce clean power for sensitive electronics.
Inverter Generators: The Clean Power Solution for Sensitive Electronics
In the realm of power generators, inverter generators stand out as the unsung heroes for powering delicate electronics. These sleek and quiet machines convert raw electrical energy into a pure sine wave, a smooth and stable waveform that mimics the electricity supplied by the grid.
Unlike traditional generators that produce a rougher modified sine wave, inverter generators provide clean power that is safe for powering laptops, TVs, medical equipment, and other sensitive devices without risking damage or interference.
Advantages of Inverter Generators
- Clean Power Output: The pure sine wave output of inverter generators ensures uninterrupted and reliable power for even the most sensitive electronics.
- Compact and Portable: Inverter generators are typically more compact and lightweight than traditional generators, making them easy to transport and store.
- Fuel-Efficient: Inverter generators utilize advanced technology to adjust their engine speed based on power demand, saving fuel and reducing emissions.
- Quiet Operation: Inverter generators operate at significantly lower noise levels compared to conventional generators, providing a less intrusive environment.
- Parallel Capability: Some inverter generators offer parallel connectivity, allowing multiple units to be linked together to increase output capacity.
Disadvantages of Inverter Generators
- Price: Inverter generators tend to be more expensive than traditional generators due to their advanced components.
- Limited Surge Capacity: Inverter generators may not be suitable for heavy-duty appliances or tools that require high surge power upon startup.
- Limited Continuous Power: The continuous power output of inverter generators may be lower than that of traditional generators, depending on the model.
Choosing the Right Inverter Generator
When selecting an inverter generator, consider the following factors:
- Wattage Requirements: Determine the combined wattage of the devices you intend to power.
- Surge Protection: Opt for a generator with surge protection to prevent damage to sensitive electronics from sudden power surges.
- Fuel Type: Inverter generators typically run on gasoline or propane. Choose a fuel that is readily available and affordable in your area.
- Portability: Consider the weight and dimensions of the generator if portability is important.
- Noise Level: Look for inverter generators with low noise ratings if noise reduction is a priority.
By carefully considering these factors, you can find an inverter generator that meets your specific needs and provides clean, reliable power for your essential electronics.
Gasoline: A Popular Yet Controversial Fuel for Generators
Gasoline, a widely accessible and affordable fuel, has long been a popular choice for powering generators. Its ease of storage and availability make it a convenient option for emergency backup and portable applications. However, gasoline also comes with its drawbacks, which should be carefully considered before making a decision.
Pros of Gasoline Generators
- Affordability: Gasoline generators are generally more affordable than their counterparts, making them an economical choice for those on a budget.
- Wide availability: Gasoline is readily available at most gas stations, ensuring easy refueling during power outages or extended periods of use.
- Simplicity of use: Gasoline generators are relatively easy to operate and require minimal maintenance, making them suitable for individuals with limited technical knowledge.
Cons of Gasoline Generators
- Fuel volatility: Gasoline is a volatile fuel that can pose fire and explosion hazards if not handled properly. Spills or leaks can be dangerous, requiring careful storage and handling.
- Short fuel life: Gasoline has a shorter shelf life compared to other fuels, losing its potency over time if not stored properly. This can lead to reduced generator performance or even starting issues.
- Environmental concerns: Gasoline combustion releases harmful emissions into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and climate change.
Gasoline remains a popular fuel choice for generators due to its affordability and accessibility. However, its limitations, such as fuel volatility, short shelf life, and environmental impact, should be carefully evaluated against the specific needs and preferences of the user. By weighing the pros and cons, individuals can make an informed decision that aligns with their circumstances and values.
Propane: The Clean-Burning Fuel for Your Generator
When choosing a fuel for your generator, propane offers several key advantages. It’s a clean-burning fuel that produces fewer emissions than gasoline or diesel, making it a more environmentally friendly option.
Propane also boasts excellent storage options. It can be stored in both liquid and vapor forms, providing flexibility in how you keep it on hand. Liquid propane is typically stored in tanks, while vapor propane can be stored in smaller containers. This versatility makes propane suitable for both home backup generators and portable generators used for camping or RVing.
Furthermore, propane is a highly efficient fuel. It burns cleanly, producing more energy per unit of fuel than gasoline or diesel. This translates to longer run times for your generator, giving you more peace of mind during power outages.
Finally, propane is relatively safe to store and handle. It’s non-toxic and doesn’t pose the same fire or explosion risks as gasoline. This makes it a good choice for generators that will be used in indoor or enclosed spaces.
Overall, propane is an excellent fuel for generators, offering a clean burn, convenient storage options, efficiency, and safety. Whether you’re looking for a backup power source for your home or a portable generator for outdoor activities, propane is a reliable and versatile choice.
Natural gas: Describe the benefits of natural gas as a fuel for generators, such as its low cost and environmental friendliness.
The Powerhouse Trio: Fueling Your Generator with Natural Gas
In the realm of backup power, generators reign supreme. And when it comes to fuel choices, natural gas stands out as a shining star. Renowned for its low cost and environmental friendliness, natural gas is an ideal fuel for powering your generator during those unexpected outages.
The Cost-Effective Champion
Natural gas is a budget-friendly option, significantly cheaper than gasoline or diesel. This difference is especially noticeable when running your generator for extended periods, making natural gas a cost-effective solution for prolonged power outages.
The Environment’s Ally
In addition to its financial benefits, natural gas is also a greener choice. Compared to gasoline and diesel, natural gas burns cleaner, producing lower emissions. This reduces air pollution and minimizes its impact on the environment, making it a responsible choice for those concerned about their carbon footprint.
Convenience at Your Fingertips
Natural gas is often piped directly to homes and businesses, providing a convenient and reliable fuel source. You won’t have to worry about running out of fuel or storing bulky tanks, ensuring hassle-free backup power when you need it most.
Whether you’re planning for an emergency or simply want to upgrade your backup power system, natural gas is an excellent fuel choice for your generator. Its low cost, environmental friendliness, and convenience make it a compelling option for households and businesses alike. Embrace the power of natural gas and ensure uninterrupted power when the lights go out!
Determining Your Generator’s Wattage: Powering Your Essential Appliances
When it comes to choosing a generator for your home or emergency needs, understanding the wattage requirements of the appliances you intend to power is paramount. It’s like planning a road trip; if you don’t know how much fuel you need, you risk running out of gas before reaching your destination. The same principle applies to generators: without knowing the wattage demands of your appliances, you could end up with a generator that’s too weak or too powerful.
Calculating Your Power Needs
The first step is to calculate the wattage requirements for the appliances you’ll be using with the generator. This involves adding up the starting wattage and running wattage of each appliance.
- Starting wattage refers to the initial surge of power needed to start an appliance. This is typically higher than the running wattage.
- Running wattage is the ongoing power consumption of an appliance while it’s in use.
For example, a refrigerator may have a starting wattage of 1,200 watts and a running wattage of 300 watts. A microwave may have a starting wattage of 1,500 watts and a running wattage of 700 watts.
Choosing the Right Generator Capacity
Once you’ve calculated the wattage requirements, it’s time to choose a generator with the appropriate capacity. The generator’s capacity, measured in watts or kilowatts (kW), should be equal to or greater than the total wattage of the appliances you’ll be powering.
- For recreational use, a generator with a capacity of 2,000 to 5,000 watts may be sufficient.
- For backup power during outages, a larger generator with a capacity of 5,000 to 10,000 watts is recommended.
- For powering heavy-duty appliances or tools, you may need a generator with a capacity of 10,000 watts or more.
Remember, it’s always better to err on the side of caution and choose a generator with a slightly higher capacity than what you think you need. This will ensure you have adequate power to handle sudden surges or unexpected electrical demands.
Generator Capacity: Powering Your Needs, from Small to Large
When choosing a generator, capacity is paramount. It determines how much power the generator can supply to your essential appliances and devices. Understanding the different generator capacities available is crucial to ensuring you pick the perfect fit for your needs.
Small Generators: Portable Power for Emergencies
- Capacity: Typically under 5,000 watts
- Usage: Perfect for powering small appliances, lights, and basic equipment during power outages or camping trips
- Benefits: Lightweight, easy to transport, and suitable for shorter-term power needs
Medium Generators: Home Backup and RV Adventures
- Capacity: 5,000 to 15,000 watts
- Usage: Suitable for powering essential appliances, lighting, and some larger devices during outages or as a backup for RVs
- Benefits: More power than small generators, can handle larger loads but still portable enough for various uses
Large Generators: Whole-House Coverage
- Capacity: Over 15,000 watts
- Usage: Designed to power an entire home during extended power outages, including major appliances, lighting, and HVAC systems
- Benefits: Provides complete power backup, ensuring comfort and safety during emergencies
Determining the Right Capacity
The key to choosing the proper generator capacity is to calculate your wattage requirements. Add up the wattage ratings of the appliances you plan to power. Consider the wattage of essential items (e.g., refrigerator, lighting) and any appliances you may want to use (e.g., air conditioner, power tools).
Overestimating is always better than underestimating. It’s better to have a generator with extra capacity to handle unexpected loads or future upgrades. However, avoid buying a generator that’s significantly larger than your needs, as it will be more expensive and less efficient.
Consult with a Professional
For larger generators, it’s highly recommended to consult with a licensed electrician. They can assess your electrical needs, recommend the appropriate capacity, and ensure that the generator is properly installed and maintained.
By understanding generator capacities and calculating your wattage requirements, you can choose the perfect generator to keep your power flowing, whether it’s for emergency backup or uninterrupted adventures.
Understanding the Importance of Hiring a Licensed Electrician for Generator Installation and Maintenance
When it comes to ensuring the safe and efficient operation of your generator, seeking the expertise of a licensed electrician is paramount. These professionals possess the knowledge, skills, and experience required to handle all aspects of generator installation and maintenance, from initial assessment to ongoing care.
Imagine this: You’ve just purchased a brand-new generator to provide peace of mind during power outages. As you eagerly unpack it, you may be tempted to tackle the installation yourself. However, doing so can be fraught with risks that could compromise your safety and the performance of your equipment.
Safety First: Avoiding Electrical Hazards
Electricity is an invisible force that can be extremely dangerous if not handled properly. Licensed electricians are trained to work safely with electrical systems, ensuring that your generator is installed and maintained without exposing you or your loved ones to electrical hazards. They know how to handle wiring, grounding, and other complex electrical components with expertise and precision.
Code Compliance: Adhering to Safety Standards
In most areas, electrical work, including generator installation, must adhere to strict building codes. Licensed electricians are familiar with these codes and will ensure that your generator system fully complies, safeguarding you against potential legal issues and ensuring the safety of your property.
Optimal Performance: Maximizing Generator Efficiency
A properly installed and maintained generator will provide optimum performance when you need it most. Licensed electricians understand the nuances of generator systems and can fine-tune them for maximum efficiency, ensuring that your appliances and electronics receive the reliable power they require.
Long-Term Savings: Preventing Costly Repairs
Regular maintenance by a licensed electrician can extend the lifespan of your generator and prevent costly repairs down the road. They can identify minor issues before they escalate into major problems, saving you both time and money in the long run.
Peace of Mind: Assured Safety and Reliability
When you hire a licensed electrician to handle your generator needs, you gain the peace of mind that your equipment is installed and maintained to the highest standards. Knowing that your family and property are safe and protected is priceless.
Don’t risk the safety of your family or the performance of your generator by attempting to do it yourself. Trust the expertise of a licensed electrician to ensure the safe and reliable operation of your generator for years to come.
Regular Maintenance: The Key to a Reliable Generator
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and optimal performance of your generator. Neglecting maintenance can lead to costly repairs or even premature failure, leaving you without power when you need it most. Here’s a comprehensive guide to the maintenance tasks you should regularly perform to keep your generator in tip-top shape:
Change the Oil and Filter
Regular oil changes are essential for any engine, including your generator. Dirty oil can cause increased wear and tear on the components, leading to reduced efficiency and potential damage. Check your generator’s manual for the recommended oil type and change interval, typically around 50-100 hours of operation.
Clean the Air Filter
A dirty air filter can restrict airflow to the engine, causing it to run less efficiently and potentially overheat. Inspect the filter regularly, especially in dusty environments, and replace it as needed. A clean air filter ensures optimal air-fuel ratio and extends the life of the engine.
Inspect Spark Plugs
Spark plugs are responsible for igniting the air-fuel mixture in the engine. Over time, spark plugs can become worn or fouled, leading to hard starting and reduced performance. Inspect the spark plugs regularly and replace them if they are damaged or exhibit excessive wear.
Check Fuel Lines and Connections
Fuel lines and connections are critical for delivering fuel to the engine. Regular inspections can help identify any leaks, cracks, or loose connections that could restrict fuel flow. Tighten any loose connections and replace damaged components as necessary.
Test the Battery
The battery provides power to start the generator. A weak or dead battery can leave you stranded when you need it most. Test the battery regularly using a voltmeter or hydrometer. If the battery is low, charge it or replace it as needed.
Inspect Cooling System
Overheating can be detrimental to your generator’s engine. Regularly check the cooling system, including the coolant level, radiator, and fan. Make sure the radiator is free of debris and the fan is operating properly.
Perform Load Testing
Load testing simulates a power outage and allows you to verify your generator’s performance under real-world conditions. Connect a load bank or appliance to the generator and gradually increase the load. This will help ensure that your generator can power your essential appliances safely and reliably.
By following these regular maintenance tasks, you can extend the lifespan of your generator, reduce costly repairs, and have peace of mind knowing that it will be there for you when the lights go out.
Generator Load Management: The Key to Preventing Overwhelm
When faced with power outages, generators come to our rescue, providing us with a lifeline of electricity. However, managing the power load on a generator is crucial to ensure its health and prevent overloading.
What is Load Management?
Load management refers to the process of monitoring and controlling the amount of power drawn from a generator. This involves balancing the power needs of appliances with the generator’s capacity to prevent overloading.
Why is Load Management Important?
Overloading a generator can lead to several problems:
- Reduced performance: The generator may struggle to provide stable power, resulting in voltage drops or fluctuations.
- Damage: Overloading can damage the generator’s internal components, shortening its lifespan.
- Safety hazards: Overheated generators can become fire hazards, posing a risk to people and property.
How to Manage Generator Load:
- Calculate power requirements: Determine the wattage of the appliances you need to power and add them up. Use this total to determine the minimum generator size required.
- Prioritize essential appliances: Decide which appliances are essential and should be powered during an outage. Focus on critical items like refrigerators, medical equipment, and lighting.
- Use energy-efficient appliances: Look for appliances with Energy Star ratings, which indicate lower power consumption.
- Unplug unused devices: Turn off and unplug devices you don’t need, such as charging cords and unused appliances.
- Monitor generator output: Keep an eye on the generator’s output power and ensure it doesn’t exceed its rated capacity.
Additional Tips:
- Consider a generator with surge protection: This can help prevent damage caused by sudden power spikes.
- Use multiple smaller generators: Instead of a single large generator, consider using several smaller ones to distribute the load and reduce the risk of overloading.
- Practice load management before an outage: Run your generator with a controlled load to test its performance and identify potential issues.
Generator load management is key to maximizing its performance, ensuring its longevity, and maintaining a safe and reliable power source. By carefully managing the power demands on your generator, you can protect your appliances, prevent generator damage, and enjoy peace of mind during power outages.