Understanding Load Wire: Comprehensive Guide For Electrical Systems
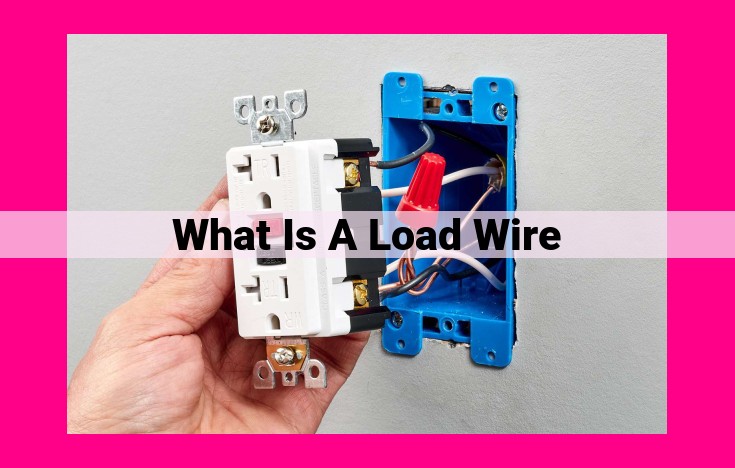
Load wire is a type of electrical wire used to carry current from a power source to electrical devices or components. It is typically made of copper or aluminum and is available in various types, including bare, insulated, stranded, and solid. Load wire is used in a wide range of applications, including electrical distribution, grounding, and fixture wiring. The electrical properties, materials, and components of load wire determine its suitability for different applications. Understanding load wire is crucial for ensuring proper installation, maintenance, and compliance with electrical standards.
Load Wire: The Foundation of Electrical Systems
In the intricate world of electricity, load wire plays a crucial role, carrying the lifeblood of power from source to destination. Understanding its types, applications, and properties is essential for ensuring safe and efficient electrical systems.
Unveiling the Types of Load Wire
The realm of load wire encompasses a diverse range of types, each tailored to specific requirements. Bare load wire stands naked, devoid of insulation, while insulated load wire sports a protective sheath safeguarding it from the elements. Stranded load wire, composed of multiple strands intertwined, offers flexibility and durability, while solid load wire remains robust and unyielding.
Exploring the Applications of Load Wire
Load wire finds its place in a myriad of industries, each harnessing its unique properties. In electrical distribution, it serves as the backbone of power transmission, carrying electricity from power plants to homes and businesses. Grounding relies on load wire to provide a safe path for stray electrical currents, preventing shocks and protecting equipment. In fixture wiring, load wire connects lighting fixtures to power sources, illuminating our spaces and enhancing safety.
Dissecting the Components and Materials of Load Wire
Load wire construction revolves around a few key materials. Copper and aluminum reign supreme as conductors, renowned for their excellent electrical conductivity. Insulators, typically made from materials like PVC, rubber, or nylon, provide protection from external elements and prevent electrical shorts.
Unveiling the Electrical Properties of Load Wire
The electrical properties of load wire govern its performance in electrical circuits. Resistance measures its opposition to current flow, capacitance relates to its ability to store electrical energy, and inductance determines its reaction to changes in current flow. Understanding these properties is crucial for designing and maintaining efficient electrical systems.
Practical Considerations: Installation and Maintenance of Load Wire
Understanding the practical considerations surrounding load wire installation and maintenance is crucial for ensuring its proper functioning and longevity. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you navigate these aspects:
Installation
Proper Handling: Load wire should be handled with care to prevent damage during installation. Avoid excessive bending or twisting, as it can compromise its integrity.
Appropriate Routing: Plan the wire’s routing carefully to avoid potential hazards and ensure efficient heat dissipation. Secure the wire firmly using appropriate supports to prevent sagging or excessive movement.
Termination Techniques: Terminating load wire securely is essential for maintaining electrical connections. Use approved connectors and follow manufacturer’s instructions to ensure a solid and reliable connection.
Maintenance
Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect load wire for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Early detection and repair can prevent potential issues and extend the wire’s lifespan.
Cleaning and Maintenance: Keep load wire clean by wiping it with a dry cloth to remove dirt and debris. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners, as they can damage the insulation.
Environmental Considerations: Load wire should be protected from extreme temperatures, moisture, and corrosive chemicals. Ensure proper ventilation and consider using moisture-resistant wire for outdoor applications.
By following these practical guidelines, you can ensure the optimal installation, maintenance, and longevity of your load wire, ensuring a safe and efficient electrical system.
External Factors
- Manufacturers and Suppliers: List reputable manufacturers and suppliers of load wire, including information on product availability and quality standards.
- Regulatory and Standards: Discuss the regulatory standards and industry guidelines that apply to load wire, ensuring compliance and safety.
External Factors: Ensuring Quality and Compliance
When selecting load wire, it’s crucial to consider manufacturers and suppliers who prioritize quality and adhere to industry standards. Reputable manufacturers use high-grade materials, employ stringent quality control measures, and maintain product availability to meet market demands. Suppliers play a vital role in ensuring timely delivery, providing technical support, and offering competitive pricing. By partnering with reputable entities, you can ensure the safety and durability of your load wire installations.
Equally important are regulatory standards and industry guidelines. Load wire must comply with these regulations to ensure public safety and system reliability. Electrical codes and standards, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) and Underwriter’s Laboratories (UL) standards, provide specific requirements for the design, installation, and maintenance of load wire. Adhering to these standards minimizes electrical hazards, protects against overheating, and ensures proper circuit operation. By staying up-to-date with regulatory changes, you can avoid potential legal liabilities and maintain compliance within your electrical systems.
Other Related Entities: Examining the Components Tied to Load Wire
When working with load wire, it’s crucial to understand the other components that play a vital role in its functionality and safety. These related entities are commonly found in electrical systems and work in conjunction with load wire to ensure proper distribution and utilization of electrical energy.
Connectors
- Connectors are devices used to *establish and maintain electrical connections* between load wire and other electrical components, such as terminals, switches, or outlets.
- They ensure a *secure and reliable electrical pathway* and come in various forms, including crimp connectors, screw terminals, and push-in connectors.
Terminals
- Terminals are connection points for load wire, providing a safe and organized way to connect multiple wires.
- They are typically made of conductive materials like brass or copper and can be found in different configurations, including screw terminals, ring terminals, and spade terminals.
Enclosures
- Enclosures provide physical protection for load wire and other electrical components, preventing damage and ensuring safety.
- They are commonly made of non-conductive materials like plastic or metal and can vary in size and shape depending on the application.
- Enclosures help maintain proper insulation and prevent accidental contact with live wires.
These related entities play a critical role in the safe and efficient operation of load wire. By understanding their function and proper use, you can ensure reliable electrical connections, enhance system performance, and *minimize electrical hazards* in your electrical setups.