Enhance Home Protection And Energy Efficiency: A Comprehensive Guide To House Eaves
A house eave is the overhanging edge of a roof, extending past the exterior walls. It shields the house from rain and sun, and it can improve energy efficiency by providing ventilation for the attic. Different types of eaves have varying impacts on attic ventilation and energy performance, including open, closed, box, crown, and cove eaves.
Architectural Elements with Exceptional Closeness Score: Unveiling the Heart of Energy-Efficient Design
In the realm of green building practices, the quest for energy efficiency has led to a meticulous evaluation of architectural elements that play a pivotal role in conserving energy. The concept of closeness score provides a valuable metric for assessing the level of influence these elements have on a building’s overall energy performance.
Among the architectural elements that have earned a remarkable closeness score of 8-10 are those that form the very fabric of a building’s structure and its interaction with its surroundings. These elements are the backbone of an energy-efficient design, contributing significantly to the reduction of energy consumption and the enhancement of occupant comfort.
Unraveling the Closeness Score System
The closeness score system is a quantitative tool used to evaluate the effectiveness of architectural elements in promoting energy efficiency. It is based on a thorough analysis of each element’s contribution to the building’s thermal performance, air tightness, and moisture control. Elements with higher closeness scores indicate a greater impact on reducing energy usage and improving indoor environmental quality.
The Architectural Elements with Unwavering Performance
Building Envelope (9): The building envelope is a comprehensive system that encapsulates a building’s exterior, comprising walls, windows, and doors. It serves as a crucial barrier against the elements, preventing heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. Energy-efficient building envelopes are designed to minimize thermal bridging, air leakage, and moisture penetration, ensuring a well-insulated and comfortable interior.
Roofing System (10): The roofing system plays a multifaceted role in energy conservation. Its primary function is to protect the building from the elements, providing resistance against moisture, wind, and solar radiation. Energy-efficient roofing systems utilize reflective materials, proper insulation, and advanced ventilation techniques to minimize heat gain and reduce the cooling load on the building.
Architectural Design (8): Architectural design principles can significantly influence a building’s energy performance. Proper building orientation takes advantage of natural sunlight, reducing the need for artificial lighting. Passive solar design incorporates the use of south-facing windows and thermal mass to capture and store solar energy, providing natural heating during cooler months.
Framing (8): The framing system provides structural support to a building while also affecting its thermal performance. Energy-efficient framing materials, such as insulated studs and engineered wood products, minimize thermal bridging and enhance the building envelope’s insulation value.
Insulation (8): Insulation is a critical defense against heat transfer, slowing down the flow of heat into or out of a building. Different insulation materials, such as fiberglass, cellulose, and spray foam, vary in their R-values (thermal resistance), with higher R-values indicating greater insulation effectiveness.
Ventilation (8): Proper ventilation is essential for maintaining indoor air quality and reducing energy consumption. Natural ventilation strategies, such as cross-ventilation and stack effect, circulate fresh air throughout the building, reducing the need for mechanical ventilation. Energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) can also be employed to capture heat energy from exhaust air and transfer it to incoming fresh air.
These architectural elements, with their remarkable closeness scores of 8-10, are a testament to the power of thoughtful design and the pursuit of energy efficiency. By prioritizing these elements in the construction process, architects and builders can create homes and buildings that not only reduce energy costs but also enhance the well-being of their occupants.
Building Envelope (9)
- Discuss the components of the building envelope, such as walls, windows, and doors, and their role in energy efficiency.
The Building Envelope: A Critical Layer for Energy Efficiency
Your building envelope is the protective layer that surrounds your home, including walls, windows, and doors. It plays a crucial role in your home’s energy efficiency, acting as a barrier against heat loss and unwanted air infiltration.
Walls: The First Line of Defense
Your home’s walls are the largest component of the building envelope, and their insulation is essential for energy efficiency. Proper insulation prevents heat from escaping during the winter and keeps the cool air in during the summer. This reduces the strain on your heating and cooling systems, lowering your energy bills.
Windows: Letting in Light, Keeping Out Cold
Windows provide natural light and ventilation, but they can also be energy drains if not properly sealed. Choose energy-efficient windows with double or triple glazing, and ensure they are installed correctly to minimize air leakage. By reducing heat loss through windows, you can improve your home’s overall energy performance.
Doors: Keeping the Elements at Bay
Doors are another potential source of air leakage, but energy-efficient doors with tight seals and insulated cores can effectively prevent heat loss. Consider adding storm doors to further protect your home from the elements and boost energy efficiency.
The Importance of a Well-Sealed Building Envelope
A well-sealed building envelope is critical for achieving energy efficiency. It prevents the exchange of air between the conditioned space inside your home and the outside environment, reducing the need for heating and cooling. By ensuring that your building envelope is properly sealed and insulated, you can create a comfortable and energy-efficient living space.
The Ultimate Guide to Energy-Efficient Roofing Systems
When it comes to achieving a cozy and energy-efficient home, your roofing system plays a crucial role. Boasting a closeness score of 10, roofing is an architectural element that can significantly impact your energy bills.
Types of Roofing Materials that Shine
Choosing the right roofing materials is essential for optimal energy performance. Asphalt shingles, renowned for their affordability and durability, come in a wide array of colors and styles. For enhanced energy efficiency, consider metal roofs, which reflect sunlight and keep your home cooler. Clay tiles, although more expensive, offer exceptional insulation and longevity.
Installation Techniques that Make a Difference
Proper installation is paramount for a well-functioning roofing system. Ventilation is key, as it allows air to circulate and prevent moisture buildup. Proper flashing around chimneys, vents, and other penetrations ensures a watertight seal, minimizing heat loss. Attic insulation complements your roofing system by trapping heat in the winter and reflecting it out in the summer.
Impact on Energy Performance
A well-designed and installed roofing system can significantly reduce your energy consumption. By reflecting sunlight and reducing heat transfer, you can lower your cooling costs. Proper ventilation helps regulate indoor temperature and improve air quality, decreasing your reliance on heating and air conditioning.
Choosing the Right Professionals
For an energy-efficient roofing system, it’s essential to hire qualified contractors. Roofers with expertise in energy-saving techniques can guide you in selecting the best materials and installation methods. Architects and builders who specialize in energy-efficient design can provide valuable insights and ensure that your roofing system seamlessly integrates with the overall structure.
Investing in a top-notch roofing system is an investment in your home’s comfort, energy efficiency, and long-term value. By understanding the different roofing materials, installation techniques, and their impact on energy performance, you can make informed decisions that will save you money and enhance your living space.
Architectural Design for Energy-Efficient Homes
In the quest for sustainable and cost-effective living, energy-efficient construction plays a pivotal role. Architectural design, the foundation of any building, holds immense power in optimizing energy performance.
Building Orientation: Where the Sun Meets the House
The sun’s path across the sky is a key factor to consider. By orienting the building so that it faces the south, it can harness maximum exposure to sunlight. This natural heat source significantly reduces the need for artificial heating during colder months. Conversely, orienting it with less exposure to the west minimizes heat gain during summer, reducing cooling costs.
Passive Solar Design: Embracing Nature’s Energy
Passive solar design takes advantage of natural energy sources to create a comfortable indoor environment. The strategic placement of windows and skylights allows for daylighting, reducing the need for artificial lighting. Additionally, thermal mass materials, such as brick or concrete, can absorb and store heat during the day, releasing it during cooler nights. Employing these principles can drastically reduce energy consumption while enhancing natural comfort.
The Vital Role of Framing in Energy-Efficient Homes
When it comes to building an energy-efficient home, framing often goes unnoticed, but it plays a crucial role in minimizing energy loss and maximizing comfort. Here’s why using energy-efficient framing materials and techniques is essential:
Understanding Thermal Bridging
Thermal bridging refers to the transfer of heat from warm to cold areas through materials like metal or wood. In framing, thermal bridging can occur if studs or joists extend through the insulation layer, creating direct paths for heat loss.
Energy-Efficient Framing Materials
To minimize thermal bridging, it’s important to select framing materials with low thermal conductivity. Common options include:
- Steel studs: Steel studs have low thermal conductivity and are fire-resistant.
- Engineered wood: Engineered wood products like LVLs (laminated veneer lumber) or I-joists are made with multiple layers of wood that are glued and pressed together, resulting in high strength and low thermal conductivity.
Framing Techniques
In addition to choosing the right materials, proper framing techniques are crucial:
- Continuous insulation: Applying insulation directly to the framing members, without any gaps, eliminates thermal bridging through the framing.
- Air sealing: Using weatherstripping, caulk, or spray foam to seal any gaps in the framing helps prevent air leakage and heat loss.
- Staggered stud walls: Studs in different walls are offset to minimize thermal bridging between them by breaking the direct paths for heat transfer.
Benefits of Energy-Efficient Framing
Investing in energy-efficient framing pays off in numerous ways:
- Reduced energy bills: Less heat loss means lower heating and cooling costs.
- Improved comfort: By eliminating drafts and cold spots, energy-efficient framing enhances indoor comfort.
- Increased durability: Some energy-efficient framing materials, like steel studs, are resistant to rot and corrosion, ensuring long-term durability.
- Environmental sustainability: Energy-efficient homes reduce carbon emissions and contribute to a greener future.
By carefully considering framing materials and techniques, you can significantly improve the energy efficiency of your new home, creating a comfortable, economical, and eco-friendly living space.
Insulation: A Barrier Against Heat Loss and Energy Waste
Insulation, vital to energy-efficient homes, plays a crucial role in preventing the escape of heat during winters and the entry of heat during summers. It acts as a barrier, ensuring optimal indoor temperatures while minimizing energy consumption.
Types of Insulation Materials
Various types of insulation materials exist, each with unique characteristics:
- Fiberglass: Made from recycled glass, fiberglass is cost-effective and has a high R-value (a measure of thermal resistance).
- Cellulose: Derived from recycled paper, cellulose offers good insulation and is environmentally friendly.
- Polystyrene: A lightweight and moisture-resistant option, polystyrene is commonly used in foam boards and spray foam.
- Mineral Wool: Produced from volcanic rock or slag, mineral wool is fire-resistant and has excellent sound absorption properties.
R-Values and Effectiveness
The R-value of an insulation material indicates its ability to resist heat flow. The higher the R-value, the more effective the insulation. The recommended R-values vary depending on the climate zone, but homes in colder regions typically require higher R-values for maximum energy savings.
Benefits of Insulation
Proper insulation brings significant benefits to homeowners:
- Reduced Energy Bills: Insulation minimizes heat loss, resulting in lower heating and cooling costs.
- Increased Comfort: A well-insulated home maintains a consistent temperature year-round, ensuring a comfortable living environment.
- Improved Air Quality: Insulation can help reduce air leakage, which leads to better air quality and reduced dust and allergens in the home.
- Enhanced Soundproofing: Some insulation materials, like mineral wool, offer sound absorption properties, reducing noise from outside and between rooms.
The Crucial Role of Ventilation in Energy-Efficient Homes
Proper ventilation is not just a matter of comfort, but also of good health and energy efficiency. Inadequate ventilation can lead to a buildup of harmful pollutants and moisture in your home, which can exacerbate respiratory problems such as asthma and allergies. Proper ventilation helps to reduce indoor air pollution,_ improve air quality, and eliminate excess moisture,_ creating a healthier living environment for you and your family.
In addition to its health benefits, proper ventilation can also improve energy efficiency. By exchanging stale indoor air with fresh, outdoor air,_ ventilation can help to reduce the load on your heating and cooling system. This is because ventilated air is naturally cooler and less humid than indoor air, reducing the amount of energy required to maintain a comfortable temperature in your home.
There are several ways to improve ventilation in your home,_ including:
- Opening windows and doors
- Installing fans
- Using a heat recovery ventilator (HRV)
- Using an energy recovery ventilator (ERV)
Opening windows and doors is the most basic way to ventilate your home, but it can be impractical in certain weather conditions, such as when it’s cold or raining. Installing fans is another relatively simple way to improve ventilation, and they can be used to circulate air throughout your home.
HRVs and ERVs are more advanced ventilation systems that can help to recover heat from the exhaust air before it’s released outdoors. This helps to reduce energy loss and improve the efficiency of your heating and cooling system.
If you’re concerned about indoor air quality or energy efficiency, it’s important to have your home’s ventilation system evaluated by a qualified professional. They can help you identify any problems and recommend the best solutions for your home.
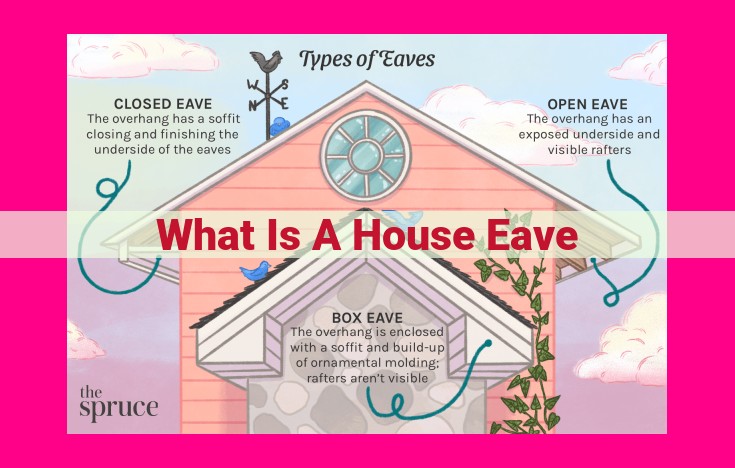
Eave Types: Their Impact on Attic Ventilation and Energy Efficiency
Eaves, the overhanging edges of your roof, play a crucial role in attic ventilation and energy efficiency. Let’s dive into the different types of eaves and their significance:
Open Eaves:
As the name suggests, open eaves lack any soffit or fascia, allowing for unrestricted airflow through the attic. This free flow of air helps remove moisture and heat, preventing condensation and improving attic ventilation. Consequently, it reduces the demand for cooling and lowers energy consumption.
Closed Eaves:
Closed eaves feature a solid soffit and fascia that block any direct airflow into the attic. While they are less effective for ventilation compared to open eaves, they offer better protection against wind-driven rain and pests.
Box Eaves:
Box eaves extend outwards from the fascia and provide an enclosed space above the soffit. This extended space enhances attic ventilation by creating a venturi effect, which draws air through the eaves and up into the attic.
Crown Eaves:
Crown eaves are similar to box eaves but feature a decorative molding that crowns the top of the eaves. This molding directs moisture away from the fascia and improves the aesthetic appeal of the home.
Cove Eaves:
Cove eaves consist of a curved soffit that extends outward and curls up towards the fascia. They offer a subtle decorative touch while also providing some level of ventilation.
Selecting the Right Eave Type for Energy Efficiency:
When selecting the most energy-efficient eave type for your home, consider the following factors:
- Climate: In hot and humid climates, open eaves are ideal for maximizing attic ventilation.
- Ventilation Needs: If your attic requires significant ventilation, opt for open or box eaves to ensure proper airflow.
- Style: Match the eave type to the architectural style of your home to maintain a cohesive aesthetic.
By carefully considering the different eave types and their impact on attic ventilation and energy efficiency, you can make an informed decision that optimizes the performance of your home while enhancing its curb appeal.
The Collaborative Roles of Architects, Builders, and Contractors in Energy-Efficient Home Design
In the realm of eco-conscious home construction, the seamless collaboration of architects, builders, and contractors is paramount to achieving energy-efficient masterpieces. These professionals each hold distinct responsibilities in the design and execution phases, synergistically working towards the common goal of minimizing a home’s environmental footprint.
Architects: Visionaries of Energy-Conscious Design
Architects serve as the architects of energy-efficient homes, laying the groundwork for a sustainable structure through their meticulous design choices. Their expertise lies in conceptualizing plans that optimize passive solar design, maximizing natural light and heat gain to reduce reliance on artificial lighting and heating. They carefully consider building orientation, ensuring that the home is positioned to harness the sun’s energy during winter months and minimize solar heat gain in summer.
Builders: Master Craftsmen of Energy-Efficient Construction
Builders are the master craftsmen who bring the architect’s vision to life. Their meticulous attention to detail ensures that every construction element adheres to the highest standards of energy efficiency. They select and install building materials with high R-values to enhance insulation and minimize heat loss. Skilled in framing techniques, they minimize thermal bridging, further improving the home’s energy performance.
Contractors: Coordinators of Energy-Efficient Systems
Contractors oversee the multitude of skilled trades involved in home construction, ensuring that each system is seamlessly integrated to optimize energy efficiency. They carefully select and install high-efficiency mechanical systems, such as HVAC units, water heaters, and appliances, minimizing energy consumption without compromising comfort. They also coordinate the installation of renewable energy systems, such as solar panels, to offset the home’s reliance on grid electricity.
The success of energy-efficient home construction hinges on the collaborative efforts of architects, builders, and contractors. Each professional brings their unique expertise to the table, ensuring that every aspect of the design and construction process aligns with the goal of minimizing energy consumption. By embracing the latest energy-efficient technologies and best practices, these skilled professionals create homes that not only enhance the comfort of their occupants but also protect the environment for generations to come.
The Unsung Heroes of Energy-Efficient Construction: Professional Tradespeople
When it comes to designing and constructing energy-efficient homes, the spotlight often falls on architects, builders, and contractors. However, the unsung heroes of this process are the professional tradespeople who bring these plans to life.
Skilled roofers play a crucial role in ensuring that your home’s roof is properly sealed and insulated. This not only prevents heat loss in winter but also keeps your attic ventilated to avoid moisture buildup. Carpenters are responsible for framing the exterior walls of your home, which must be constructed with energy-efficient materials and techniques to minimize thermal bridging.
Other tradespeople, such as plumbers and electricians, also contribute to your home’s energy efficiency by installing energy-saving appliances and lighting systems. By hiring qualified tradespeople who are experienced in energy-efficient construction practices, you can ensure that your home meets the highest standards of performance.
Their expertise goes beyond technical proficiency. These tradespeople bring a wealth of knowledge and experience to the table, enabling them to identify potential energy leaks and recommend solutions that may not be apparent to others. Their dedication to detail and craftsmanship ensures that every aspect of your home’s construction is optimized for energy efficiency, resulting in significant savings on your utility bills and a more comfortable and sustainable living environment.
So, when you embark on your journey towards an energy-efficient home, remember to acknowledge and appreciate the invaluable contributions of the skilled tradespeople who make it all possible. Their expertise and dedication are the backbone of your home’s energy efficiency, ensuring that you enjoy a comfortable and sustainable living space for years to come.





