Plasterboard (Drywall): The Ultimate Guide For Interior Construction
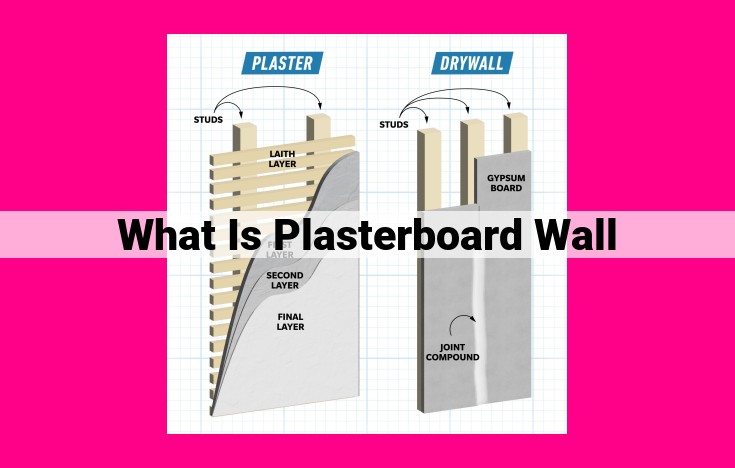
Plasterboard, also known as drywall, is a versatile construction material composed of a gypsum core encased in paper facing. It is primarily used for constructing interior walls and ceilings, providing a smooth and durable surface for painting, wallpapering, or other finishes. Plasterboard installation involves framing and mounting it to studs or joists, with joints reinforced using joint compound and sanded to create a seamless appearance. Its fire-resistant, sound-absorbing, and decorative properties extend its applications, while its sustainability and ease of repair make it an economical choice for both residential and commercial buildings.
Plasterboard: The Unsung Hero of Construction
In the bustling realm of construction, there exists an unsung hero that silently shapes the very spaces we inhabit: plasterboard. This versatile and indispensable material has revolutionized the way we build, offering countless benefits that enhance our living environments. Plasterboard, also known as drywall or gypsum board, holds a pivotal place in modern construction, playing a crucial role in everything from residential homes to towering skyscrapers.
What is Plasterboard?
Plasterboard is a lightweight, fire-resistant material made from a gypsum core sandwiched between two sheets of heavy paper or fiberboard. The gypsum core is primarily composed of calcium sulfate, a mineral that provides strength and stability. The paper facing serves to protect the core and provide a surface for painting and other finishes.
Significance in Construction
Plasterboard’s significance in construction stems from its numerous advantages. It is:
- Versatile: Plasterboard can be used for walls, ceilings, soffits, and a wide range of other applications.
- Fire-Resistant: Its gypsum core provides excellent fire resistance, delaying the spread of flames.
- Lightweight: Its lightweight makes it easy to handle and install, reducing labor costs.
- Sound-Absorbing: Some types of plasterboard offer sound-absorbing properties, creating quieter living spaces.
- Energy-Efficient: Plasterboard helps insulate buildings, reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling.
Materials and Components: The Building Blocks of Plasterboard
Plasterboard, a versatile material indispensable in modern construction, is composed of a trio of essential components: a gypsum core, paper facing, and a range of additives.
1. Gypsum Core: The Heart of Plasterboard
The core of plasterboard is crafted from calcium sulfate dihydrate, a compound more commonly known as gypsum. This mineral, mined from natural deposits, provides the material with its strength and rigidity. The gypsum core, when combined with water, forms a hard and durable surface that resists fire and sound.
2. Paper Facing: The Protective Shield
Enveloping the gypsum core is a layer of paper facing. This paper, typically made from recycled materials, serves as both a protective barrier and a bonding surface. The paper facing prevents moisture and air from penetrating the core, ensuring its long-lasting integrity.
3. Additives: Enhancing Performance
To enhance the performance of plasterboard, a variety of additives are incorporated into the gypsum core. These additives, each with a specific function, contribute to the material’s durability, flexibility, and resistance to fire and sound. For instance, starch is added to improve board strength, while fiberglass strands reinforce the core, preventing it from cracking under stress.
Essential Tools and Equipment for Masterful Plasterboard Installation
When embarking on a plasterboard installation project, having the right tools and equipment is paramount for ensuring precision, efficiency, and a professional-looking finish. Let’s explore the indispensable tools that will empower you to conquer your plasterboard endeavors.
Plasterboard Saws: A Sharp Edge for Precision Cuts
Plasterboard saws are specialized tools designed to effortlessly cut through plasterboard, leaving clean and precise edges. From manual saws to electric saws, there’s a range of options to suit your needs and preferences. Choose a saw that offers a comfortable grip and a sharp blade to minimize effort and maximize accuracy.
Drills and Screws: Secure Connections, Effortless Installation
Drills and screws play a crucial role in securing plasterboard to framing and other surfaces. Invest in a reliable drill with a variety of bits to accommodate different screw sizes and types. Opt for screws specifically designed for plasterboard, ensuring a strong hold without damaging the material.
Drywall Lifts: Ergonomic Handling, Heavier Loads
When installing large sheets of plasterboard, drywall lifts prove invaluable. These specialized devices provide a safe and ergonomic method for lifting and positioning plasterboard sheets, reducing strain and fatigue. They come in various configurations, offering options to handle different heights and weights.
Construction Techniques: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to constructing walls and ceilings, plasterboard, also known as drywall, plays a crucial role. Its versatility and ease of installation make it a popular choice in residential and commercial buildings alike. Understanding the construction techniques involved in working with plasterboard will ensure your project is completed to the highest standards.
Framing and Installation
The first step is to create a framework of wooden studs that will support the plasterboard panels. These studs should be spaced at regular intervals, typically 16 or 24 inches apart. The panels are then attached to the studs using screws or nails. It’s important to ensure that the panels are flush with each other to create a smooth surface.
Joint Compound Application
Once the plasterboard is in place, the joints between the panels need to be sealed and smoothed. This is done using a joint compound, which is a type of plaster that fills and covers the joints. The compound is applied in multiple layers, each of which is allowed to dry before the next is applied.
Sanding and Finishing
After the joint compound has dried, it is sanded to create a smooth and uniform surface. This step is crucial for achieving a professional-looking finish. Fine-grit sandpaper is used to remove any imperfections and ensure that the joints are completely invisible. The walls and ceilings can then be painted or wallpapered to match the desired decor.
By following these construction techniques, you can ensure that your plasterboard installation is both durable and aesthetically pleasing. From framing and installation to sanding and finishing, each step plays a vital role in creating a long-lasting and beautiful surface.
Advanced Plasterboard Applications: Enhancing Your Construction Projects
In the realm of construction, plasterboard, also known as drywall, reigns supreme as a versatile and indispensable material. Beyond its standard uses, advanced plasterboard applications elevate its capabilities to meet the demanding requirements of contemporary building projects.
One such application is fire-resistant plasterboard, which stands as a guardian against the devastating consequences of fire. Its specialized composition safeguards occupants and structures by containing flames and preventing their spread. This vital feature makes it an essential choice for high-risk areas such as kitchens, furnace rooms, and commercial buildings.
For environments seeking acoustic tranquility, soundproofing plasterboard emerges as a game-changer. Its dense construction absorbs and deflects sound waves, creating a serene atmosphere. This remarkable property makes it the perfect solution for recording studios, home theaters, and public spaces seeking noise reduction.
Finally, decorative plasterboard transcends the realm of functionality, introducing an artistic flair to interior design. With intricate patterns, textured surfaces, and vibrant colors, it transforms walls into captivating focal points. Whether it’s a living room accent wall or a commercial building’s lobby, decorative plasterboard empowers architects and designers to express their creativity.
These advanced plasterboard applications not only enhance construction projects but also cater to the evolving needs of modern society. They provide crucial safety measures, improve acoustic comfort, and enable aesthetic possibilities, making plasterboard an indispensable tool in the construction toolbox.
Maintenance and Repair of Plasterboard
Plasterboard walls and ceilings are an integral part of any home, and while they are relatively durable, they can become damaged over time. Fortunately, repairing and maintaining plasterboard is a relatively inexpensive and straightforward process.
Patching and Repairing Holes
Small holes in plasterboard can be easily patched using a spackling paste or a drywall repair kit. Simply apply the paste or compound to the hole and smooth it out with a putty knife. Once the patch has dried, sand it smooth and repaint the area.
For larger holes, you may need to cut out a section of the plasterboard and replace it with a new piece. To do this, use a drywall saw to cut a square or rectangular hole around the damaged area. Then, cut a new piece of plasterboard to fit the hole and screw it into place. Finally, apply joint compound to the seams and sand it smooth.
Repainting and Refinishing
Over time, plasterboard walls and ceilings can become dirty or faded. To restore their original appearance, you can repaint them using a latex-based paint. Before painting, be sure to clean the walls and ceilings with a damp cloth to remove any dirt or dust.
If the plasterboard is badly damaged, you may need to refinish it before painting. This involves removing the old paint and applying a new coat of primer. Once the primer has dried, you can paint the plasterboard with your desired color.
By following these simple tips, you can easily maintain and repair your plasterboard walls and ceilings, keeping them looking their best for years to come.
Environmental Considerations for Plasterboard: Sustainability and Indoor Air Quality
Sustainability and Recycling of Plasterboard
Plasterboard, also known as drywall or gypsum board, is a versatile building material with a significant environmental impact. As construction practices evolve, sustainability becomes paramount. Plasterboard manufacturers are exploring innovative ways to reduce their ecological footprint.
One key aspect of sustainability is recycling. Plasterboard is highly recyclable, contributing to the circular economy. Recycled plasterboard can be used as a raw material for the production of new plasterboard or other building products. By reusing and recycling plasterboard, we conserve natural resources and reduce landfill waste.
Indoor Air Quality Concerns
Plasterboard has been associated with potential indoor air quality concerns, primarily due to the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during installation and over time. VOCs can contribute to respiratory irritation and other health issues.
To address these concerns, manufacturers have developed low-VOC and no-VOC plasterboard products. These products significantly reduce VOC emissions, creating a healthier indoor environment. Additionally, proper ventilation during installation and regular maintenance can further mitigate indoor air quality concerns associated with plasterboard.
Responsible Construction Practices
By choosing sustainable and low-VOC plasterboard products, contractors can contribute to greener and healthier buildings. Proper installation techniques and regular maintenance ensure that plasterboard remains an environmentally friendly choice throughout its lifecycle.
As the construction industry continues to emphasize sustainable construction practices, plasterboard manufacturers are striving to develop even more eco-friendly and health-conscious products. By embracing these innovations, we can build a more sustainable and healthier built environment for generations to come.
Market Trends and Innovations in Plasterboard
The plasterboard industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and sustainable construction practices emerging to meet the demands of the modern construction sector.
One of the most significant trends is the development of new plasterboard technologies, such as lightweight and moisture-resistant boards. These innovative materials offer improved performance and can be used in a wider range of applications, making them ideal for contemporary building projects.
Another key trend is the increasing focus on sustainable construction practices. Plasterboard manufacturers are developing eco-friendly products that have a reduced environmental impact. These products may be made from recycled materials or incorporate sustainable manufacturing processes, allowing builders to create environmentally responsible structures.
Here are a few specific examples of new plasterboard technologies and sustainable construction practices:
- Lightweight plasterboard: This type of plasterboard is lighter than traditional drywall, making it easier to handle and install. It is also more durable and can withstand higher levels of vibration.
- Moisture-resistant plasterboard: This type of plasterboard is treated with a water-resistant coating, making it ideal for use in bathrooms, kitchens, and other areas with high humidity.
- Recycled plasterboard: This type of plasterboard is made from recycled materials, reducing waste and helping to conserve natural resources.
- Sustainable manufacturing processes: Some plasterboard manufacturers are using sustainable manufacturing processes, such as reducing energy consumption and using renewable energy sources.
These market trends and innovations are shaping the future of the plasterboard industry, making it more sustainable, efficient, and versatile than ever before. As a result, construction professionals have access to a wider range of products and technologies to meet the needs of any project.





