Understanding Bright Indirect Light: Essential For Plant Growth
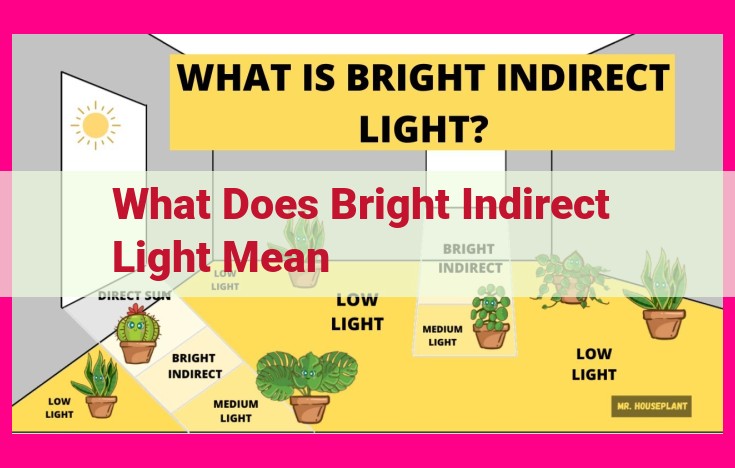
Bright indirect light refers to light that is bright but not direct. It comes from a source that is not in direct line of sight, such as light that has been reflected off walls, ceilings, or other surfaces. Plants that require bright indirect light thrive in areas with plenty of natural light but without prolonged exposure to harsh direct sunlight. This type of lighting provides even illumination and helps prevent sunburn or bleaching of the plant’s leaves.
Lighting Sources: The Vital Essence for Indoor Plant Growth
As avid plant enthusiasts, we know that providing our leafy companions with the ideal environment is crucial for their well-being. Among the essential factors, lighting stands out as a fundamental pillar for thriving indoor plants. Let’s delve into the realm of lighting sources and understand how to harness their power for optimal plant growth.
Natural Light: Nature’s Blessing for Plants
Natural light, the radiant glow of the sun, provides a myriad of benefits for plants:
- Energy Source: Through photosynthesis, plants transform sunlight into essential energy for their biological processes.
- Brightness: Natural light offers the full spectrum of wavelengths, providing a balanced source of illumination.
- Duration: Sunlight exposure varies with seasons and location, ensuring plants receive adequate light during peak growth periods.
- Direction: Plants can adjust their growth patterns towards the direction of light, promoting even growth.
Artificial Light: A Reliable Substitute When Nature Fails
When natural light is scarce, artificial light sources step in as reliable substitutes:
- Fluorescent Lights: These energy-efficient bulbs emit a wide range of wavelengths, making them suitable for general plant growth.
- LED Lights: Highly efficient and long-lasting, LEDs provide a targeted spectrum of light that can be customized for specific plant needs.
- High-Intensity Discharge (HID) Lights: These powerful lights emit intense, concentrated light, ideal for fast-growing or high-light plants.
The Vital Elixir of Light: A Guide to Essential Plant Care
Light, the lifeblood of our vibrant green companions, plays an indispensable role in their very existence. This radiant energy not only fuels photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and carbohydrates, but also influences their growth, development, and overall well-being.
Photosynthesis: The Foundation of Plant Growth
At the heart of the plant’s life cycle lies photosynthesis, a remarkable process that transforms sunlight into nourishment. Within the plant’s intricate green cells, chlorophyll, a pigment that absorbs specific wavelengths of light, captures the sun’s rays and converts them into chemical energy. This energy then fuels the plant’s growth and development, ensuring its vitality and exuberance.
Photomorphogenesis: Shaping the Plant Form
Beyond photosynthesis, light also exerts a profound influence on photomorphogenesis, the process by which plants respond to light signals by modifying their growth and development. This is most evident in the striking differences between plants grown in low-light and high-light conditions. In low-light environments, plants often exhibit elongated stems in an attempt to reach available light, while in high-light environments, they develop shorter, bushier structures to optimize light absorption.
Understanding Plant Light Requirements
Every plant species has its own unique light requirements, ranging from those that thrive in the dappled shade of a canopy to those that flourish in the intense glare of direct sunlight. Determining the optimal light conditions for your plants is crucial for their success. Consider factors such as the origin of the plant (tropical, temperate, sub-tropical) and its natural habitat (forest floor, open meadow, etc.). Research and observe to identify the light levels that best suit your plant companions.
Adjusting Light for Plant Needs
Once you have determined the light requirements of your plants, it’s essential to provide them with light that meets their specific needs. If natural light is limited, consider supplementing with artificial light sources, such as fluorescent, LED, or high-intensity discharge (HID) lamps. These lights emit specific wavelengths of light that can mimic natural sunlight and promote healthy plant growth. By adjusting the intensity, duration, and wavelength of light, you can cater to the unique needs of your plant family, ensuring their continued prosperity and well-being.
Light Characteristics: The Key to Plant Growth and Development
Understanding the Language of Light
To nurture thriving plants in your interior spaces, it’s crucial to delve into the realm of light characteristics. These elements determine how light behaves and affects plants. Just like words in a language, the properties of light can be understood by breaking them down into four essential components: intensity, duration, wavelength, and spectral quality.
Light Intensity: The Power of Brilliance
Imagine your plants basking in the warm glow of the sun. The intensity of light, measured in lux or foot-candles, dictates the amount of photosynthetic energy available to plants. High-intensity light, like that found in direct sunlight, fuels rapid growth, while low-intensity light encourages slower, more compact growth. Tailoring light intensity to the needs of specific plant species is key to optimal growth and health.
Light Duration: The Rhythm of Day and Night
Every living thing has an internal clock, and plants are no exception. The duration of light exposure, measured in hours, influences plant development and hormone production. Most plants thrive under a cycle of light and dark, with the duration varying depending on the species. Understanding the light requirements of your plants is essential for creating a harmonious environment that supports their natural rhythms.
Light Wavelength: The Spectrum of Colors
White light is a vibrant tapestry of colors, each with a unique wavelength. Different wavelengths trigger different responses in plants. Blue light, found in abundance during the early morning and evening, promotes stem elongation and leaf development. Red light, prevalent at sunrise and sunset, stimulates flowering and fruit production. Understanding the effects of different wavelengths allows you to optimize light for specific plant needs and create a vibrant indoor oasis.
Spectral Quality: The Fine-Tuning of Light
Spectral quality refers to the distribution of wavelengths within a light source. Different light sources emit unique spectral profiles that can influence plant growth and development. For instance, fluorescent lights emit a narrow spectrum, which can be limiting for some plant species. On the other hand, LED lights offer a more tunable spectrum, allowing you to customize the light to match the specific needs of your plants.
Optimizing Light Characteristics for Different Plant Species
The optimal light characteristics for your plants depend on their species and growth stage. By understanding the unique requirements of each plant, you can tailor the light environment to maximize their potential. For example, low-light plants like ferns and snake plants can thrive in shady corners or under indirect sunlight. High-light plants like succulents and cacti need plenty of bright, direct light to flourish. By providing the right light characteristics, you can create a sanctuary where your plants can thrive and bring a touch of nature into your home.
Plant Lighting in Interior Design
When incorporating living greenery into your interior décor, lighting plays a pivotal role in ensuring the well-being of your plant companions. Understanding the lighting needs of different species is crucial for their optimal growth and aesthetic appeal.
Light Considerations for Plant Integration
Consider the natural light availability of your intended plant placement. Rooms with ample windows facing south or west offer optimal natural light, while those with north or east-facing windows may require supplementary lighting. Artificial lighting can compensate for limited natural light and provide the necessary intensity and duration for plant growth.
Plant Selection for Lighting Conditions
When selecting plants for your space, choose species suited to the available lighting. Low-light tolerant plants, such as snake plants, ZZ plants, and peace lilies, can thrive in rooms with limited natural light. For areas with abundant light, consider leafy plants like ferns, palms, and ficus trees.
Artificial Lighting to Enhance Growth
Artificial grow lights can be used to supplement natural light or provide illumination in low-light areas. Choose energy-efficient LED lights that emit the appropriate wavelengths for plant growth. Experiment with different light intensities and durations to find the optimal settings for your plants. By tailoring lighting to specific plant needs, you can foster lush indoor gardens that add life and beauty to your living space.





